Patent Examination System
Accelerated Examination
According to Article 61 of the Korean Patent Act, the Minister of the Ministry of Intellectual Property may direct an examiner to examine one application in preference over another if it falls under any one of the following types or circumstances:
1. Where a person, other than the applicant, is commercially and industrially working the invention claimed in a patent application after the laying-open of the application; or
2. Where the Minister of the Ministry of Intellectual Property deems it necessary to urgently process a patent application prescribed by Presidential Decree:
3. Where a patent application prescribed by Presidential Decree is deemed necessary for disaster prevention, response, recovery, etc.
① "Patent application prescribed by Presidential Decree" in subparagraph 2 of Article 61 of the Act means a patent application designated by the Minister of the Ministry of Intellectual Property, among the following patent applications: ⟨Amended on Apr. 19, 2022⟨
a. A patent application in the area of the defense industry;
b. A patent application directly related to green technology under the Framework Act on Carbon Neutrality and Green Growth For Coping with Climate Crisis;
c. A patent application directly related to export promotion;
d. A patent application concerning the official duties of the State or local governments (including any patent application concerning the duties of the national and public schools provided for in the Higher Education Act, which is filed by the organization in charge of the technology transfer and industrialization established within the national and public schools pursuant to Article 11 (1) of the Technology Transfer and Commercialization Promotion Act);
e. A patent application filed by an enterprise falling under any one of the following items, provided, however, that the claimed invention is related to its business type and at least one applicant belongs to the enterprise when the patent application is originally filed;
(1) A patent application filed by an enterprise confirmed as a venture business under Article 25 of the Act on Special Measures for the Promotion of Venture Businesses;
(2) A patent application filed by an enterprise selected as a technology-innovative small and medium enterprise under Article 15 of the Act on the Promotion of Technology Innovation of Small and Medium Enterprises;
(3) A patent application filed by an enterprise selected as an exemplary company in terms of the employee invention compensation system under Article 11-2 of the Invention Promotion Act;
(4) A patent application filed by a small or medium enterprise with the certification for management of intellectual property under Article 24-2 of the Invention Promotion Act;
f. A patent application concerning the results of national research and development programs under subparagraph 1 of Article 2 of the National Research and Development Innovation Act;
g. A patent application which serves as a basis of a priority claim under Treaties (limited to cases where a patent is being processed by a foreign patent office, upon a priority claim based on the relevant patent application);
h. A patent application under which an invention is being practiced or being prepared to be practiced by the patent applicant;
i. A patent application directly related to a specialized business to which the regulatory sandbox is applied under Article 55 of the��Regulatory Sandbox Act on Regulation-Free Zone and Regional Special Development Zone��
j. A patent application related to medical R&D carried out within a high-tech medical complex filed by a medical R&D institution to which the regulatory sandbox is applied under Article 26 of the��Special Act on the Promotion of High-Tech Medical Complexes��
k. A patent application mainly for prevention or elimination of pollution, referring to an environmental pollution prevention facility or applied measure(s) by the facility falling under any one of the following items;
l. A patent application filed by any one of the following persons:
(1) A person aged 65 or older;
(2) A person whose health problem is likely to incapacitate him or her from following the procedure relating to a patent until a decision is rendered as to whether to grant a patent or to reject a patent application unless he or she expedites the prosecution.
m. A patent application utilizing artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), 3D printing, autonomous vehicle, Big Data, cloud computing, intelligent robot, smart city, virtual reality/augmented reality (VR/AR), innovative medicine, new renewable energy, customized healthcare, drone, next generation telecommunications, intelligent semiconductor, high-tech materials and blockchain technology, assigned with 4IR related new patent classification designated by the Ministry of Intellectual Property as presented in appended Table 3
n. An international patent application for which the Ministry of Intellectual Property conducts international search as an International Searching Authority (ISA) under the Patent Cooperation Treaty pursuant to Article 198-2 of the Act;
o. A patent application related to high technologies, such as semiconductor, etc., essential to a national economy and national competitiveness (limited to the applications publicly notified by the Minister of the Ministry of Intellectual Property in designation of subjects and petition period for accelerated examination)
② A patent application on which the Minister of the Ministry of Intellectual Property has agreed with the counterpart of any foreign patent office to preferentially examine;
③ A patent application regarding which a person who intends to file a petition for accelerated examination requested a specialized agency designated and publicly notified as a specialized agency for search and classification to conduct a search for prior art with respect to the pending application and has requested the specialized agency to notify the Minister of the Ministry of Intellectual Property of the search results;
④ "Patent application prescribed by Presidential Decree" in subparagraph 3 of Article 61 of the Korean Patent Act means any one of the following patent applications: ⟨Newly Inserted on Jun. 22, 2021⟩
a. Any one of the following patent applications determined and publicly notified by the Minister of the Ministry of Intellectual Property:
(1) A patent application directly related to products for medical treatment and disease control under subparagraph 21 of Article 2 of the Infectious Disease Control and Prevention Act;
(2) A patent application directly related to disaster safety products certified under Article 73-4 of the Framework Act on the Management of Disasters and Safety;
(3) A patent application subject to a public notice given by the Minister of the Ministry of Intellectual Property for a specified period of applying for accelerated examination in response to an emergency situation caused by a disaster.
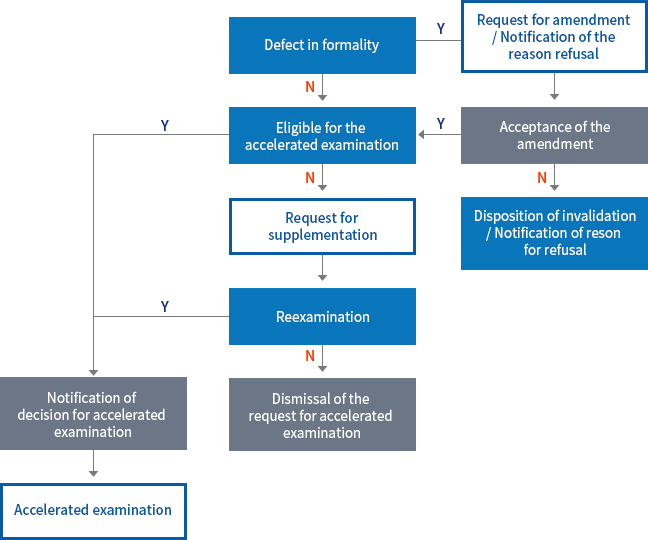
An applicant desiring to expedite his/her application under the accelerated examination program must submit a written request containing a statement explaining the necessity in detail and any supporting evidence.
⟨Flow Chart of Accelerated Examination⟩
Deferred Examination System
- An applicant may request deferred examination within 9 months from the date of filing a request for examination, if necessary. The applicant can choose the initiation date of the deferred examination which must take place at least 2 years after the examination request and within 5 years of the application date. The applicant will receive the first office action from the Ministry of Intellectual Property within 3 months from the date when the deferred examination is initiated.
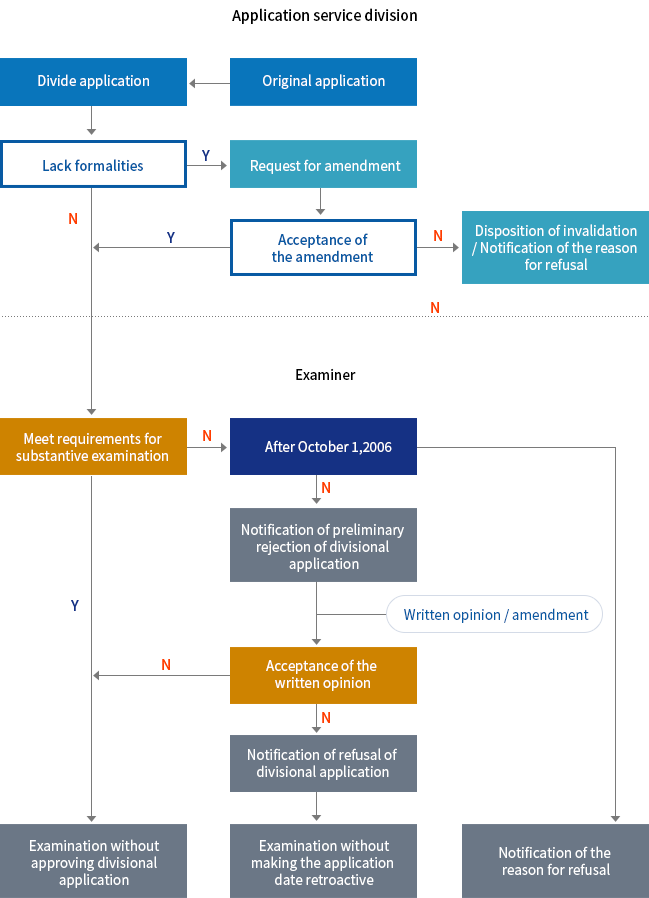
Divisional application
- An applicant who has filed a patent application comprising of two or more inventions may divide the application into multiple applications.
⟨Flow Chart of Divisional Application⟩
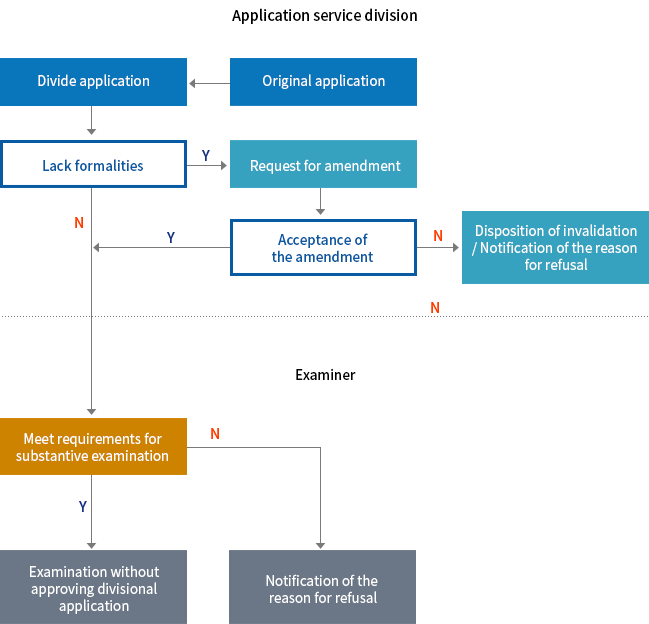
Converted Application
- An applicant may convert a patent application to a utility model application or vice versa within 30 days from the date on which the applicant received a certified copy of the first non-final rejection.
⟨Flow Chart of Converted Application⟩
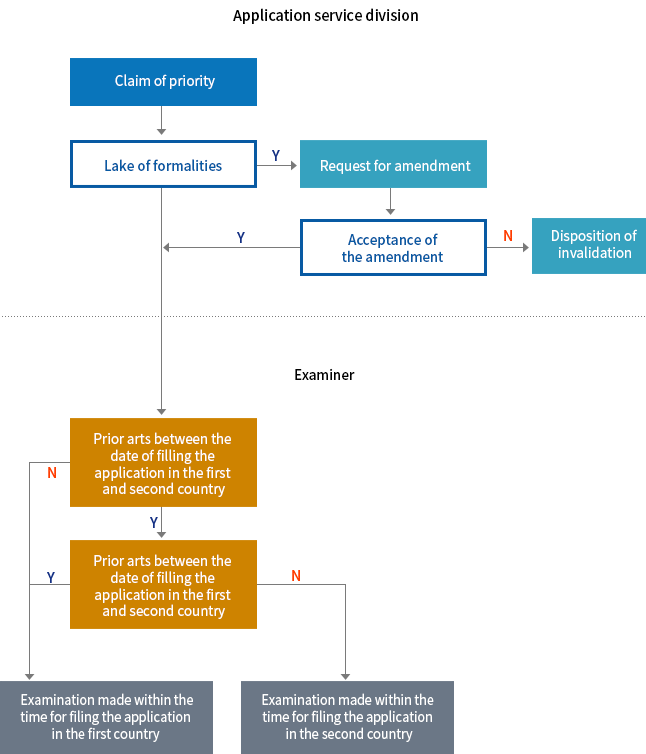
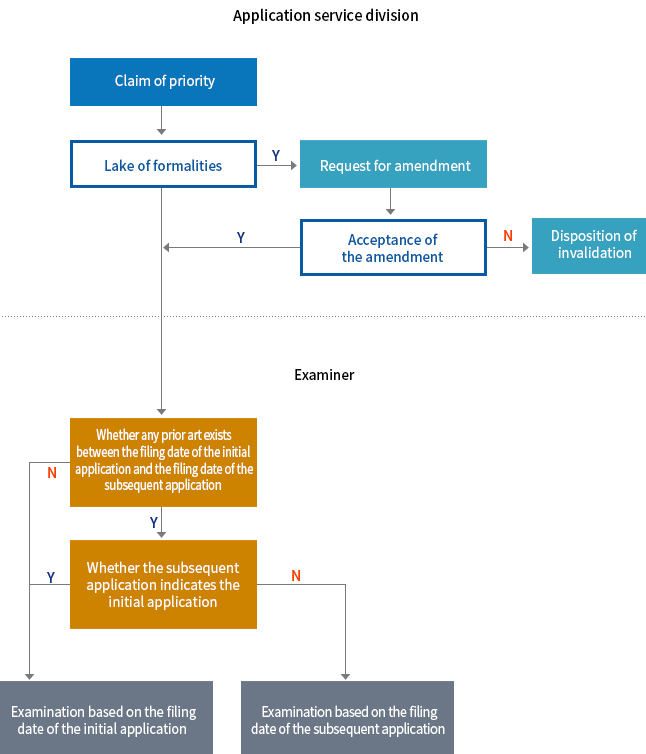
Priority Claim under the Treaty
- It is a recognized system by the Paris Convention and the member states of the WTO to make a priority claim under the Treaty. Whenever an application filed in one country is filed again in another member state within 1 year of the first filing date, the filing date of the original application is retroactively applied to the subsequent application.
⟨Flow Chart of Priority Claim under the Treaty⟩
Domestic Priority Claim
- An applicant may make a priority claim based on an invention described in the specification or drawings initially attached to an earlier application of a patent or utility model registration within 1 year of the date of filing the earlier application for which he/she has the right to obtain a patent.
⟨Flow Chart of Domestic Priority Claim⟩
Ex-officio Amendment
- If an examiner determines that an application is patentable but there are clear clerical errors in the specification, drawings, or an abstract attached to such patent application, for example, misspellings or wrong reference numbers, the examiner can make an ex officio correction of the error without having to request the applicant to submit a written response (For a granted patent after July 1, 2009).
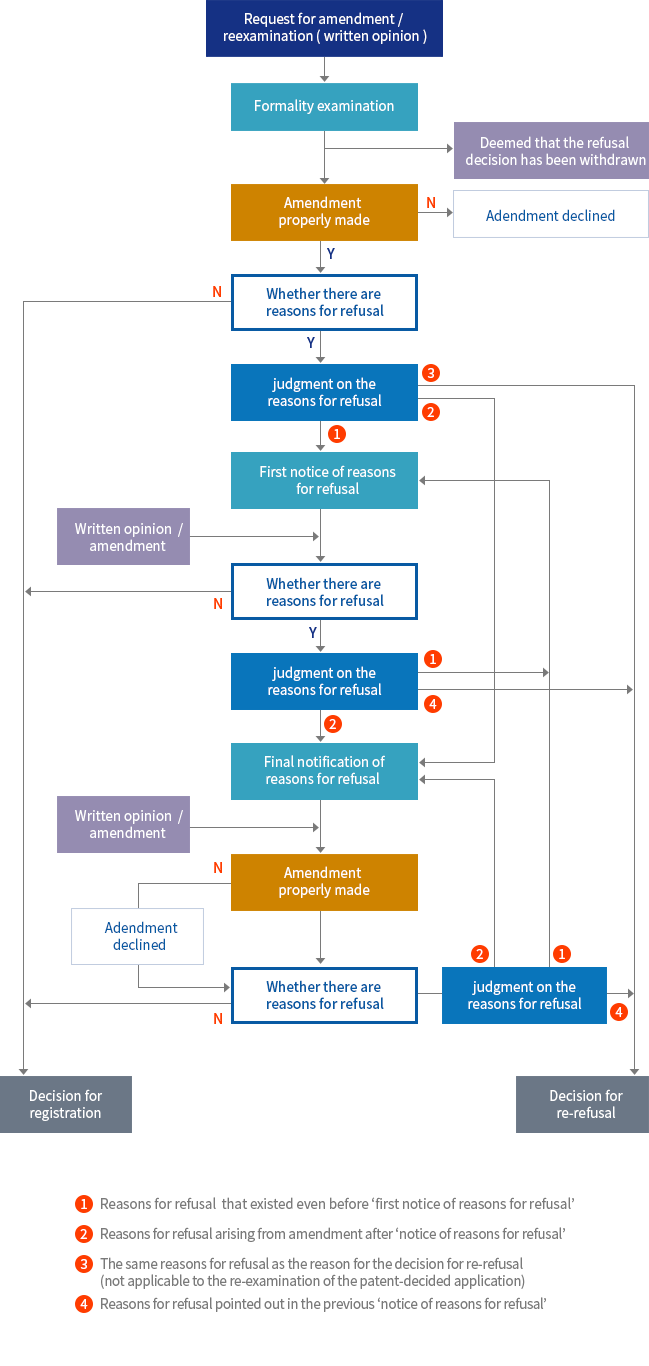
Request for Reexamination (Before a Trial)
- Under the re-examination system, an examiner can re-examine an amended application, where an applicant amended a specification or drawing(s) of an application within a certain period of time after the grant or disposal of an application initially granted with a patent or rejected as unpatentable.
⟨Flow chart of a reexamination before a trial⟩
First Office Action Pendency
- The first office action pendency is calculated from the date when a request for examination is filed to the date when the examination is started. Prolonged pendency to the first office action delays the enforcement of rights and hinders the commercialization and profitability of new technologies.
- For these reasons, KIPO has made seamless efforts to shorten the FOA pendency. Specifically it has increased its number of patent examiners, expanded its outsourcing of prior art searches and maximized its examination capabilities by introducing an automatic search system, etc. As a result of those efforts, KIPO currently provides the world's fastest patent examination service.
- Average First Office Action Pendency for Patent and Utility Models
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
| Pendency period (months) | 10.4 | 10.3 | 10.8 | 11.1 | 12.2 | 14.4 |
- Last updated 27 April 2023
- Patent Legal Administration Division
